Polish People's Army
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
The Polish People's Army (Polish: Ludowe Wojsko Polskie, pronounced [luˈdɔvɛ ˈvɔjskɔ ˈpɔlskʲɛ]; LWP)[1] was the second formation of the Polish Armed Forces in the East during the latter stages of the Second World War (1943–1945), and subsequently the armed forces of the Polish communist state (1945–1989), which was formalized in 1952 as the Polish People's Republic.[2]
The creation of communist-led Polish armed forces that were outside the command of the Polish government-in-exile was allowed and facilitated by Soviet leader Joseph Stalin, following efforts made in the early 1940s by Soviet-based Polish exiles Wanda Wasilewska and Zygmunt Berling.
Initially called the Polish Army in the USSR from 1943 to 1944,[3] it became the Polish Troops[4] and Armed Forces of the Republic of Poland[5] from 1944 to 1952, and thereafter the Armed Forces of the Polish People's Republic.[6] During these restructurings, the Polish military was increasingly integrated into Soviet military and command structures, becoming comparatively more distinct and independent in 1956.
On 7 October 1950, the anniversary of the Battle of Lenino—one of the first major engagements of Polish Armed Forces in the East against Axis forces—was declared the official "Day of the Polish People's Army" by the People's Republic.
History
[edit]World War II
[edit]
What became the LWP was formed during World War II, in May 1943, as the 1st Tadeusz Kościuszko Infantry Division, which developed into the First Polish Army, unofficially known as Berling's Army. Because of the shortage of Polish officers and the policies of the Soviet Union, in March 1945 Soviet Red Army officers accounted for nearly 52% of the officer corps (15,492 out of 29,372). Around 4,600 of them remained in the LWP by July 1946.[7]
It was not the only Polish formation that fought on the Allied side, nor the first one formed in the East. The earlier Polish force formed in the Soviet Union, known as Anders' Army, was loyal to the Polish government-in-exile and by that time had moved to Iran. The communist-led Polish forces soon grew beyond the 1st Division into two major commands – the First Polish Army (initially under Zygmunt Berling) and the Second Polish Army (commanded by Karol Świerczewski). The First Polish Army participated in the Vistula–Oder Offensive, the Battle of Kolberg and the final Battle of Berlin.[1]
Immediate post-war years
[edit]


After the war the Polish Army was reorganized into six (later seven) military districts. These were the Warsaw Military District, headquartered (HQ) in Warsaw, the Lublin Military District, HQ in Lublin, the Kraków Military District, HQ in Kraków, the Łódź Military District, HQ in Łódź, the Poznań Military District, HQ in Poznań, the Pomeranian Military District, HQ in Toruń, and the Silesian Military District, HQ in Katowice.[citation needed]
In the late 1940s and early 1950s, the Polish Army was under the command of Marshal of the Soviet Union, Marshal of Poland and Minister of Defense of Poland Konstantin Rokossovsky. It was increasingly integrated into Soviet military structure and organization. This process was mitigated in the aftermath of the Polish October of 1956, when Władysław Gomułka formalized aspects of Poland's military relationship with the Soviet Union.[8] The Sovietization of the armed forces structure was phased out altogether and thus the combat and service support structures were integrated once more into regular combat formations following the old Polish model.
Cold War
[edit]
An anti-Zionist purge in the Polish Army took place in 1968 to systematically remove soldiers of Jewish origin, following the Six-Day War between Israel and Arab countries.
Characteristics
[edit]Uniform
[edit]In 1949, the first fundamental uniform reform after the war was made.[9] The "Dress Rules for the Soldiers of the Polish Army" were introduced and were to apply from January 1, 1951.
In the Polish People's Army, a soft field cap modeled on the pre-war one was introduced. After the war, the pre-war garrison caps were used again. Stiffened caps were only worn until around 1950 when they were completely replaced by round caps. In 1982, the Polish Rogatywka, modeled on the pattern from 1935, were restored in the Polish Army's Representative Company.[10]
Chaplaincy
[edit]Throughout the entire period of the existence of the Polish People's Army, its officers and soldiers were provided with pastoral care. Such a service was provided by the General Dean's Office of the Polish Army.[11]
Training
[edit]In the 1980s, the Polish People's Republic had 4 military academies and 11 higher officers' schools, which trained auxiliary corpsmen and corresponded in rank to higher educational institutions. In 1954, judo instructors from the Warsaw and Kraków institutes of physical culture, participated in the training program for border guards and military personnel of the airborne units of the Polish army.[12]
Equipment
[edit]| Weapon | Origin | Type | Notes | Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-64 | Semi-automatic pistol | 
| ||
| P-83 | Semi-automatic pistol | |||
| P-33[13] | Semi-automatic pistol | Licensed copy of TT-33. | 
| |
| AKM | Assault rifle | Standard issue rifle | 
| |
| PM-84 | Submachine gun | Limited use | 
| |
| PM-63 | Submachine gun | Standard submachine gun form 1963 till 1989[14] | 
| |
| 7.62 mm pm wz.41 | Submachine gun | Polish PPSh-41 produced domestically.[15] | 
| |
| SWD | Designated sniper rifle | Standard marksman rifle of PPA | 
| |
| PK | General purpose machinegun | Standard general purpose machinegun of PPA | 
| |
| SKS | Semi-automatic rifle | [16] | 
| |
| Mosin–Nagant | Bolt-action rifle | Domestically produced.[17] | 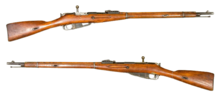
| |
| SG-43 Goryunov | Machine gun | [18] | 
| |
| RPG-7 | Light AT weapon | 
|
Ground Forces
[edit]| Tank | Origin | Version | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-60 | 3 pcs. - 1944-1945[19][20] | After the war, several pieces were sent to military schools.[21] | ||
| T-70 | 53 pcs. - 1944-1945[22] | Some of the tanks used after 1945 by the Internal Security Corps.[23] | ||
| T-34 | 1940, 1941, 1942, 1943[24] | 118 pcs. - 1944-1945[25] | According to Magnuski, many different versions of the T-34 vehicle were used, both early production and modernized ones.[26] | |
| T-34-85 | M1, M2[27] | 328 pcs. - 1944–1945. 1083 pcs. - 1955, 1444 pcs. - 1960, 417 pcs. - 1985[28] | Domestically produced 1355 pcs. between 1952 and 1956.
In 1985, the military had 417 pieces of M1, M2 versions.[29] | |
| PT-76 | PT-76, PT-76B[30] | 68 pcs. - 1965, 108 pcs. - 1970, 112 pcs. - 1985, 30 pcs. 1990[31] | Some of the tanks were modernized in Poland by adding a DSzK HMG above the loader's hatch.[32] | |
| T-54 | A, AD, AM, AM1, AM2, T-55U[33] | 1258 pcs. - 1965, 998 pcs. - 1970[34] | Between 1956 and 1964, 2,000 T-54 tanks were produced under license in Poland.[35] | |
| T-55 | A, AD, AD-1, AD-2, AM, AD1M, AD2M, AMS[36] | 128 pcs. - 1965, 956 pcs. - 1970, 2653 pcs., 2100 pcs. - 1990[37] | Between 1964 and 1980, 5,000 T-55s were produced. Most of it was exported.[38] | |
| T-72 | M, M1[39] | 317 pcs. - 1985, 700 pcs. - 1990[40] | In the years 1981–1990, Zakłady Mechaniczne Bumar-Łabędy produced approximately 1,600 T-72 tanks.[41] | |
| IS-2 | M[42] | 50 pcs. - 1944–1945,[43][44] 180 pcs. - 1955, 75 pcs. - 1960[45] | Withdrawn from use in the 1960s.[46] | |
| IS-3 | 2 or 3 pcs.[47] | Brought for testing purposes. They did not come into use. Two copies have been preserved in museums in Poznań and Warsaw.[48] |
| TD/SPG | Origin | Version | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU-57 | SPG | 15 pcs. - 1944–1945,[49] Few pcs. survived war.[50] | Withdrawn from use in the 1950s.[51] | |
| SU-76 | SPG | 130 pcs. - 1944–1945,[52] 206 pcs. - 1955.[53] | Withdrawn from use in the 1950s.[54] | |
| SU-85 | TD | 70 pcs. - 1944–1945,[55] 51 pcs. - 1955, 43 pcs. - 1960[56] | Withdrawn from use in the 1960s.[57] | |
| SU-100 | TD | At least 3 pcs. - 1943-1945[58] | Withdrawn from use in the 1950s.[59] | |
| ISU-122S | SPG | 32 pcs. – 1944–1945,[60] 399 pcs. (together with ISU-152) – 1955, 49 pcs. – 1960[61] | Withdrawn from use in the 1960s.[62] | |
| SU-152 | SPG | 3 pcs. - 1944-1945[63] | ||
| ISU-152 | SPG | 10 pcs. – 1944–1945,[64] 399 pcs. (together with ISU-122S) – 1955[65] | Withdrawn from use in the 1950s.[66] | |
| ASU-85 | SPG | 20-30 pcs. - 1965-1975[67] | Withdrawn from use in the second half of 1970s.[68] | |
| 2S1 Goździk | SPG | 166 pcs. - 1985, 490 pcs. - 1990[69] | Licensed production launched in the 1980s at Huta Stalowa Wola.[70] | |
| wz.77 DANA | SPG | The first copies appeared in WP in the mid-1980s.[71] |
| APC/IFV | Origin | Version | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BWP-1 | IFV | 1 400[72] | ||
| BMP-2 | IFV | 62[73] | Sold to Angola after communism fell in country.[74] | |
| MT-LB | APC | 15 | [75] | |
| TOPAS | WPT-TOPAS, -2AP, R-2, R-3[76] | 120 pcs. - 1968, 70 pcs. - 1990[76] | Jointly developed by Poland and Czechoslovakia[77] | |
| SKOT | -1A, -2A, S-260 Art, S-260 Inż., -WPT, -2AP, R-1, R-2, R2M, R2AM, R-3, R-3M, R-3AM, R-4, R-6[76] | 548 pcs. - 1966
2 500 total production form Polish Army[78] |
Jointly developed by Poland and Czechoslovakia between 1963 and 1971.[76] | |
| BTR-60 | PU-12[79] | Included with the 9K33 Osa SAM system delivered between 1980 and 1985.[79] | ||
| BRDM-1 | The first ones entered the army in the 1960s[76] | |||
| BRDM-2 | 9P133, 9P148, RS, 9P31[77] | 800 pcs. - 1990[76] | ||
| FUG | The first ones entered the army in the 1960s[77] |
Air Force
[edit]| Model | Origin | Type | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MiG-21 | Fighter | 600 | [80] | |
| MiG-23 | Fighter | 40 | [80] | |
| MiG-29 | Fighter | 12 | [80] | |
| Sukhoi Su-7 | Attack Aircraft | 50 | [80] | |
| Su-20 | Attack Aircraft | 40 | [81] | |
| Sukhoi Su-22 | Attack Aircraft | 110 | [81] | |
| Ilyushin Il-28 | Bomber | 80 | [81] | |
| Antonov An-2 | Transport | N/A | [81] | |
| Antonov An-26 | Transport | 20 | ||
| Ilyushin Il-14 | Transport | 30 | ||
| Mil Mi-8 | Helicopter | 80 | ||
| Mil Mi-2 | Helicopter | 200 | [82] | |
| Mil Mi-24 | Attack helicopter | 40 |
Artillery
[edit]Rocket Artillery
[edit]- RM-70- 30[83]
- BM-21 Grad-250 in 1980s.
- 9K52 Luna-M- 40 launchers in 1980s[83]
- Scud B- 25 launchers in 1980s [84]
Towed artillery
[edit]Selfpropelled artillery
[edit]- 2S1 Gvozdika-498[84]
- 152 mm SpGH DANA- 111[84]
- 2S7 Pion-8[83]
Air defense
[edit]Mobile missile
[edit]Mobile self-propelled AA guns
[edit]- ZSU-23-4 Shilka-150 were delivered from USSR until 1991[86]
Towed anti-aircraft gun
Engagements
[edit]- Battle of Lenino - 1943
- Battle of Studzianki - 1944
- Vistula-Oder offensive - 1945
- Battle of Kolberg - 1945
- Siege of Danzig - 1945
- Battle of Bautzen - 1945
- Battle of Berlin - 1945
- Anti-communist resistance in Poland (1944–1946)
- Battles for Bircza - 1945–1946
- Operation Vistula - 1947
- Poznań protests of 1956
- Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia - 1968
- Polish protests of 1970
- Pacification of Wujek - 1981
- Martial law in Poland (13 December 1981 – 22 July 1983)
See also
[edit]- Air Force of the Polish Army
- Polish Armed Forces
- Polish Armed Forces (Second Polish Republic)
- Main Directorate of Information of the Polish Army (GZI WP)
- Internal Military Service (WSW)
- Border Protection Troops (WOP)
- Polish Legions (Napoleonic period)
- Polish Military Organisation
- Armia Ludowa
- Gwardia Ludowa
- Polish forces in the West
- Polish forces in the East
- First Polish Army (1944–1945)
References
[edit]- ^ a b Popularna Encyklopedia Powszechna Wydawnictwa Fogra (2016). "Pierwsza Armia Wojska Polskiego". Encyklopedia WIEM. Archived from the original on 2016-11-06. Retrieved 2016-11-06.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Initially ruled by the Polish Workers' Party (1942-1948) and thereafter the Polish United Workers' Party.
- ^ Polish: Armia Polska w ZSRR.
- ^ Polish: Wojsko Polskie
- ^ Polish: Siły Zbrojne Rzeczpospolitej Polskiej.
- ^ Polish: Siły Zbrojne Polskiej Rzeczypospolitej Ludowej
- ^ Kałużny, Ryszard (2007). "Oficerowie Armii Radzieckiej w wojskach lądowych w Polsce 1945-1956". Zeszyty Naukowe WSOWL (in Polish). 2 (2). AWL: 86–87. ISSN 1731-8157.
- ^ Jerzy Eisler, Siedmiu wspaniałych poczet pierwszych sekretarzy KC PZPR [The Magnificent Seven: First Secretaries of KC PZPR], Wydawnictwo Czerwone i Czarne, Warszawa 2014, ISBN 978-83-7700-042-7, pp. 214–215
- ^ Dziennik rozkazów MON nr 4 z 1949 roku poz.30.
- ^ "Pulk Reprezentacyjny Wojska Polskiego". Archived from the original on 2022-12-07. Retrieved 2021-06-08.
- ^ "Duszpasterstwo wojskowe w PRL". sjerzy.parafia.info.pl. Retrieved 2017-09-04.
- ^ Влодзимеж Голембевский. Из-под Фудзиямы на Вислу // журнал «Польша», № 5 (117), май 1964. стр.52-53
- ^ Instrukcja Piechoty Pistolet wz. 1933 (wydanie drugie) Piech. 38/48 [Infantry Manual Pistol pattern. 1933 (second edition) Piech. 38/48] (in Polish) (2nd ed.). Poland: Wydawnictwo Ministerstwa Obrony Narodowej. 18 October 1961.
- ^ Ministerstwo Obrony Narodowej - Departament Uzbrojenia (1974). 9 mm PISTOLET MASZYNOWY wz.1963 OPIS I UŻYTKOWANIE SPOSOBY I ZASADY STRZELANIA Uzbr. 1048/68 [9 mm MACHINE PISTOL wz.1963 DESCRIPTION AND USE SHOOTING METHODS AND RULES Armed. 1048/68] (in Polish) (Wydanie z 1974 ed.). Poland: Wydawnictwo Ministerstwa Obrony Narodowej.
- ^ https://web.archive.org/web/20131214032102/http://www.fabrykabroni.pl/tresci.php. Archived from the original on 2013-12-14. Retrieved 2024-07-06.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ "Artigo original com identificação". doi:10.33233/eb.v17i5.2331.s1537 (inactive 2024-11-04). Retrieved 2024-07-06.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ^ "Mosin Nagant Master Model Reference". 2017-07-16. Archived from the original on 2017-07-16. Retrieved 2024-07-06.
- ^ Smith 1969, p. 526.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Magnuski, Janusz; Modrzewski, Jerzy (1985). Wozy bojowe LWP [Ludowego Wojska Polskiego]: 1943-1983. Warszawa: Wydaw. Min. Obrony Narodowej. ISBN 978-83-11-06990-9.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Magnuski, Janusz; Modrzewski, Jerzy (1985). Wozy bojowe LWP [Ludowego Wojska Polskiego]: 1943-1983. Warszawa: Wydaw. Min. Obrony Narodowej. ISBN 978-83-11-06990-9.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Magnuski, Janusz; Modrzewski, Jerzy (1985). Wozy bojowe LWP [Ludowego Wojska Polskiego]: 1943-1983. Warszawa: Wydaw. Min. Obrony Narodowej. ISBN 978-83-11-06990-9.
- ^ Magnuski, Janusz; Modrzewski, Jerzy (1985). Wozy bojowe LWP [Ludowego Wojska Polskiego]: 1943-1983. Warszawa: Wydaw. Min. Obrony Narodowej. ISBN 978-83-11-06990-9.
- ^ Magnuski, Janusz; Modrzewski, Jerzy (1985). Wozy bojowe LWP [Ludowego Wojska Polskiego]: 1943-1983. Warszawa: Wydaw. Min. Obrony Narodowej. ISBN 978-83-11-06990-9.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Magnuski, Janusz (1985). Wozy bojowe LWP: 1943 - 1983. Warszawa: Wydawn. Min. Obrony Nar. ISBN 978-83-11-06990-9.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Magnuski, Janusz; Modrzewski, Jerzy (1985). Wozy bojowe LWP [Ludowego Wojska Polskiego]: 1943-1983. Warszawa: Wydaw. Min. Obrony Narodowej. ISBN 978-83-11-06990-9.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Magnuski, Janusz; Modrzewski, Jerzy (1985). Wozy bojowe LWP [Ludowego Wojska Polskiego]: 1943-1983. Warszawa: Wydaw. Min. Obrony Narodowej. ISBN 978-83-11-06990-9.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Magnuski, Janusz; Modrzewski, Jerzy (1985). Wozy bojowe LWP [Ludowego Wojska Polskiego]: 1943-1983. Warszawa: Wydaw. Min. Obrony Narodowej. ISBN 978-83-11-06990-9.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Magnuski, Janusz; Modrzewski, Jerzy (1985). Wozy bojowe LWP [Ludowego Wojska Polskiego]: 1943-1983. Warszawa: Wydaw. Min. Obrony Narodowej. ISBN 978-83-11-06990-9.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Magnuski, Janusz; Modrzewski, Jerzy (1985). Wozy bojowe LWP [Ludowego Wojska Polskiego]: 1943-1983. Warszawa: Wydaw. Min. Obrony Narodowej. ISBN 978-83-11-06990-9.
- ^ Magnuski, Janusz; Modrzewski, Jerzy (1985). Wozy bojowe LWP [Ludowego Wojska Polskiego]: 1943-1983. Warszawa: Wydaw. Min. Obrony Narodowej. ISBN 978-83-11-06990-9.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2017). Czołgi i samobieżne działa pancerne Wojska Polskiego 1919-2016. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-249-0.
- ^ bocquelet, david. "Polish Tanks & AFVs of the Cold War". tanks-encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 2024-07-06.
- ^ BMP-2 Pancerni.net 1 Archived 18 August 2007 at the Wayback Machine. Pancerni.abajt.pl. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
- ^ "Polish Land Forces from 1945 - Muzeum Wojsk Lądowych". Retrieved 2024-07-06.
- ^ a b The Military Balance 2017, p. 145.
- ^ a b c d e f Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2014). Pojazdy Ludowego Wojska Polskiego (Wydanie I ed.). Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-192-9.
- ^ a b c Szczerbicki, Tomasz (2014). Pojazdy Ludowego Wojska Polskiego. Czerwonak: Vesper. ISBN 978-83-7731-192-9.
- ^ Kubiaczyk C., Transporter opancerzony SKOT, A. Karaś, W. Stefanowska (red.), J. Magnuski, Seria: Typy broni i uzbrojenia, vol. 9, Warszawa: Wydawnictwo Ministerstwa Obrony Narodowej, 1971
- ^ a b "BTR-60", Wikipedia, 2024-06-26, retrieved 2024-07-10
- ^ a b c d "Orbats". www.scramble.nl. Retrieved 2024-07-07.
- ^ a b c d World Air Forces 1971 pg. 935. UK: FlightGlobal. 1971. p. 935. Archived from the original on 2015-07-08. Retrieved 2021-01-08.
- ^ Hoyle and Farfad Flight International 10–16 December 2019, p. 47.
- ^ a b c d "Poland - Army Equipment". www.globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 2024-07-06.
- ^ a b c d "Poland - Army Equipment". premium.globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 2024-07-06.
- ^ "9K33 Osa (1972)". truck-encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 2024-07-06.
- ^ "5. ЗЕНИТНЫЕ САМОХОДНЫЕ УСТАНОВКИ (ЗСУ) – Военный паритет". www.militaryparitet.com. Archived from the original on 28 July 2017. Retrieved 22 May 2017.
Sources
[edit]- Smith, Joseph E. (1969). Small Arms of the World (11 ed.). Harrisburg, Pennsylvania: The Stackpole Company. ISBN 9780811715669.
- The Military Balance 2017. Arundel House, Temple Place, London, UK: International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS). 2017. ISBN 978-1-85743-900-7. OCLC 960838207 – via Routledge.
External links
[edit] Media related to Ludowe Wojsko Polskie at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ludowe Wojsko Polskie at Wikimedia Commons- Maps showing the LWP positioning
- Personnel policy of the LWP in the post-war period


